The importance of Spatial Thinking in Surgery Training

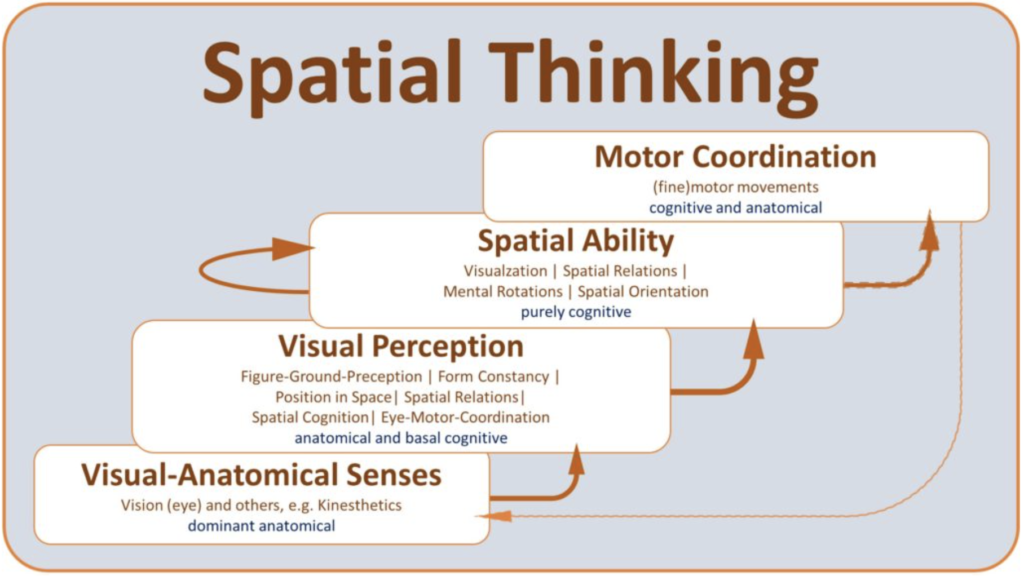
The term “Spatial Thinking” is a concept, covering various facets like spatial perception, spatial ability, visual perception, and spatial intelligence. It includes how these skills enable individuals to interpret and manipulate spatial information mentally. This involves receiving and processing optical stimuli, recognizing spatial objects, mentally manipulating these objects, and executing spatial motor movements. Spatial thinking is a unifying term for these interconnected abilities, crucial for activities requiring spatial understanding and manipulation, like ophthalmological surgery.
In relation to surgery training, spatial thinking is particularly relevant. Surgeons must be adept at visualizing and manipulating three-dimensional structures mentally, understanding spatial relationships in the human body, and accurately executing complex motor tasks.
The development of spatial thinking skills can significantly enhance a surgeon’s ability to perform surgical procedures effectively, as it directly correlates with the ability to understand, interpret, and navigate the complex and variable eye anatomy of patients.
Enhancing spatial thinking in surgical training can be approached through various methods. These include the use of three-dimensional models, virtual reality simulations, and targeted exercises designed to improve spatial perception and manipulation. By incorporating these techniques into surgical education, trainees can develop a more intuitive grasp of anatomical structures and improve their ability to perform precise and safe surgical interventions.
Overall, the integration of spatial thinking training into eye surgical education represents a significant advancement in preparing surgeons for the complex and dynamic nature of surgeries. It equips them with essential cognitive tools to visualize, interpret, and manipulate anatomical structures, leading to improved surgical outcomes and patient care.